Description
Isolate RNA with a Simple, 1-hour Procedure
The SV Total RNA Isolation System provides a fast and simple technique for preparation of intact total RNA from tissues, cultured cells and white blood cells in as little as one hour. Using this membrane-based purification system, up to 60mg of tissue can be processed per purification, depending on tissue type. The system incorporates a DNase treatment step directly on the minicolumn membrane. This step substantially reduces genomic DNA contamination, which can interfere with amplification-based methodologies. Purification is achieved without the use of phenol:chloroform extractions or ethanol precipitations, and there is no DNase carryover in the final RNA preparation
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Fresh whole blood | Yes | Yes | A protocol is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Brisco, P. Sankbeil, J. and Kephart, D. (1997) Promega Notes 64, 7–10 Hara, N. et al. (2002) Clin. Cancer Res. 8, 1794–9. PubMed ID #12060619. |
| Human blood plasma and serum | Yes | Yes | A protocol is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resource: Fresh or once-frozen human serum (100μl) was added to 175μl of SV RNA Lysis Buffer, then the remainder of the SV Total RNA Isolation System protocol was followed. Chen, X.Q. et al. (2000) Clin. Cancer Res. 6, 3823–6. PubMed ID #11051224. |
| Human leukocytes | Yes | A protocol is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. | |
| Winter flounder red blood cells | Yes | Pedersen, S.F. et al. (2003) Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 284, C1561–76. PubMed ID #12734109. | |
| Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells | Yes | Yawalker, N. et al. (1998) J. Invest. Dermatol. 111, 1053–7. PubMed ID #9856816. Escoffier, C. et al. (1999) J. Virol. 73, 1695–8. PubMed ID #9882382. | |
| Primary CD4+ human T lymphocytes | Yes | Secchiero, P. et al. (2000) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 14620–5. PubMed ID #11114167. | |
| Viral RNA from human plasma | Yes | Personal communication. Contact Promega Technical Services for more information. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Mammalian tissues | A general protocol for total RNA isolation from tissue is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources are listed below | ||
| Mouse or rat brain | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Kephart, D. Measuring gene expression from mammalian brain tissue. eNotes Brisco, P. Sankbeil, J. and Kephart, D. (1997) Promega Notes 64, 7–10 Kephart, D. and Hooper, K. (1998) Promega Notes 69, 17–9. Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. |
| Mouse thoracic dorsal root ganglion neurons | Yes | Ekström, P.A.R. et al. (2003) Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 22, 383–95. PubMed ID #12691739. | |
| Mouse central nervous system | Yes | Serafini, B. et al. (2000) Am. J. Pathol. 157, 1991–2002. PubMed ID #11106572. | |
| Mouse small intestine | Yes | Serafini, B. et al. (2000) Am. J. Pathol. 157, 1991–2002. PubMed ID #11106572. Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. | |
| Mouse muscle | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Sakai, H. et al. (1999) J. Physiol. 519, 323–33. PubMed ID #10457052. Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. |
| Mouse or rat liver | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Sakai, H. et al. (1999) J. Physiol. 519, 323–33. PubMed ID #10457052. Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. |
| Mouse kidney | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. Attmane-Elakeb, A. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 33548–53. PubMed ID #10942780. |
| Mouse spleen | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Serafini, B. et al. (2000) Am. J. Pathol. 157, 1991–2002. PubMed ID #11106572. Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. |
| Mouse embryonic heart, brain and skeletal muscle | Yes | Agarkova, I. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10256–64. PubMed ID #10744711. | |
| Mouse or rat lung | Yes | Yes | Agarkova, I. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10256–64. PubMed ID #10744711. |
| Rat pancreas | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Brisco, P. Sankbeil, J. and Kephart, D. (1997) Promega Notes 64, 7–10. Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. | |
| Mouse or rat heart | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Brisco, P. Sankbeil, J. and Kephart, D. (1997) Promega Notes 64, 7–10. Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. |
| Mouse colon | Yes | Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. | |
| Mouse stomach | Yes | Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. | |
| Mouse thymus | Yes | Pinto, D. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6476–82. PubMed ID #10037740. | |
| Mouse eyes | Yes | Lucas, R.J. et al. (1999) Science 284, 505–7. PubMed ID #10205062. | |
| Mouse retina | Yes | Freedman, M.S. et al. (1999) Science 284, 502–4. PubMed ID #10205061. | |
| Rat whole cochlea, modiola and cochlear sensorineural epithelial/lateral walls | Yes | Stöver, T. et al. (2000) Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 76, 25–35. PubMed ID #10719212. | |
| Human muscle | Yes | Roth, S.M. et al. (2002) Physiol. Genomics 10, 181–90. PubMed ID #12209020. | |
| Human placenta | Yes | Neuschäfer-Rube, F. et al. (2003) Biochem. J. 371, 443–9. PubMed ID #12519077. Gonzalez-Perrett, S. et al. (2001) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 1182–7. PubMed ID #11252306. | |
| Human skin | Yes | Yawalker, N. et al. (1999) J. Invest. Dermatol. 113, 43–8. PubMed ID #10417617. Yawalker, N. et al. (1998) J. Invest. Dermatol. 111, 1053–7. PubMed ID #9856816. | |
| Human brain | Yes | Miyasaka, T. et al. (2001) Am. J. Pathol. 158, 373–9. PubMed ID #11159174. | |
| Primary human peritoneal mesothelial cells | Yes | Cronauer, M.V. et al. (1999) Am. J. Pathol. 155, 1977–84. PubMed ID #10595927. | |
| Human cerebrovascular tissue | Yes | Cronauer, M.V. et al. (1999) Am. J. Pathol. 155, 1977–84. PubMed ID #10595927. | |
| Human adenoma tissue | Yes | Jaquet, P. et al. (2000) J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 781–92. PubMed ID #10690891. | |
| Human hair follicle | Yes | Use fresh samples and at least 10 or more hair roots. Align the hairs, and cut the root end from the hair and quickly process using the SV RNA Isolation System. The amount of RNA is very small and can generally only be detected by RT-PCR. Contact Promega Technical Services for more information. | |
| Ferret aorta | Yes | Gangopadhyay, S.S. et al. (2002) Biochem. J. 372, 347–57. PubMed ID #12603201. | |
| Feline oral mucosa | Yes | Harley, R. et al. (1999) Clin. Diag. Lab. Immunol. 6, 471–8. PubMed ID #10391845. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Plant tissues | A general protocol for total RNA isolation from plant tissue is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources are listed below. | ||
| Tomato leaf | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Shenoi, H. and Kephart, D. Titration of tomato leaf material used as starting material for SV total RNA isolation. eNotes Kobs, G. (1998) Promega Notes 68, 28–31. | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana leaf | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Technically Speaking: SV Total RNA Isolation System. Promega Notes 68, 16–9.Caldelari, D. et al. (2001) Plant Physiol. 126, 1416–29.PubMed ID #11500541. |
| Arabidopsis thaliana flower, stem and root | Yes | Caldelari, D. et al. (2001) Plant Physiol. 126, 1416–29. PubMed ID #11500541. | |
| Tobacco leaf | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. | |
| Sugar beet 14-day seedling, cotyledon, hypocotyl, 46-day plant and 90-day plant) | Yes | Fowler, M.R. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Bot. 353, 2125–6. PubMed ID #11141186. | |
| Chicory taproot, etiolated heads, leaf, and green and etiolated seedlings | Yes | Fowler, M.R. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Bot. 353, 2125–6. PubMed ID #11141186. | |
| Three-day-old mung bean hypocotyls | Yes | Leiter, H. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21830–9. PubMed ID #10419500. | |
| Pea seedling leaf | Yes | Skaf, J.S. et al. (2000) J. Gen. Virol. 81, 1103–9. PubMed ID #10725438. | |
| Plant tissues | A general protocol for total RNA isolation from plant tissue is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources are listed below. | ||
| Tomato leaf | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Shenoi, H. and Kephart, D. Titration of tomato leaf material used as starting material for SV total RNA isolation. eNotes Kobs, G. (1998) Promega Notes 68, 28–31. | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana leaf | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Technically Speaking: SV Total RNA Isolation System. Promega Notes 68, 16–9.Caldelari, D. et al. (2001) Plant Physiol. 126, 1416–29.PubMed ID #11500541. |
| Arabidopsis thaliana flower, stem and root | Yes | Caldelari, D. et al. (2001) Plant Physiol. 126, 1416–29. PubMed ID #11500541. | |
| Tobacco leaf | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. | |
| Sugar beet 14-day seedling, cotyledon, hypocotyl, 46-day plant and 90-day plant) | Yes | Fowler, M.R. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Bot. 353, 2125–6. PubMed ID #11141186. | |
| Chicory taproot, etiolated heads, leaf, and green and etiolated seedlings | Yes | Fowler, M.R. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Bot. 353, 2125–6. PubMed ID #11141186. | |
| Three-day-old mung bean hypocotyls | Yes | Leiter, H. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21830–9. PubMed ID #10419500. | |
| Pea seedling leaf | Yes | Skaf, J.S. et al. (2000) J. Gen. Virol. 81, 1103–9. PubMed ID #10725438. | |
| Plant tissues | A general protocol for total RNA isolation from plant tissue is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources are listed below. | ||
| Tomato leaf | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Shenoi, H. and Kephart, D. Titration of tomato leaf material used as starting material for SV total RNA isolation. eNotes Kobs, G. (1998) Promega Notes 68, 28–31. | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana leaf | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Technically Speaking: SV Total RNA Isolation System. Promega Notes 68, 16–9.Caldelari, D. et al. (2001) Plant Physiol. 126, 1416–29.PubMed ID #11500541. |
| Arabidopsis thaliana flower, stem and root | Yes | Caldelari, D. et al. (2001) Plant Physiol. 126, 1416–29. PubMed ID #11500541. | |
| Tobacco leaf | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for plant tissue in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. | |
| Sugar beet 14-day seedling, cotyledon, hypocotyl, 46-day plant and 90-day plant) | Yes | Fowler, M.R. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Bot. 353, 2125–6. PubMed ID #11141186. | |
| Chicory taproot, etiolated heads, leaf, and green and etiolated seedlings | Yes | Fowler, M.R. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Bot. 353, 2125–6. PubMed ID #11141186. | |
| Three-day-old mung bean hypocotyls | Yes | Leiter, H. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21830–9. PubMed ID #10419500. | |
| Pea seedling leaf | Yes | Skaf, J.S. et al. (2000) J. Gen. Virol. 81, 1103–9. PubMed ID #10725438. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Cultured cells (Established cell lines are not listed.) | Yes | A general protocol for total RNA isolation from mammalian cultured cells is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources are listed below. | |
| Primary rat endothelial cells | Yes | Thum, T., Haverich, A. and Borlak, J. (2000) FASEB J. 14, 740–51. PubMed ID #10744630. | |
| Fibroblasts derived from mouse embryonic stem cells | Yes | Zhang, S., Day, I.N.M. and Ye, S. (2001) Physiol. Genomics 5, 187–92. PubMed ID #11328964. | |
| Primary human coronary artery endothelial cells | Yes | Zhang, S., Day, I.N.M. and Ye, S. (2001) Physiol. Genomics 5, 187–92. PubMed ID #11328964. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Bacteria | A general protocol for total RNA isolation from Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources are listed below. | ||
| Escherichia coli | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for bacteria in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Kobs, G. (1998) Promega Notes 68, 28–31. Ohmichi, T., Maki, A. and Kool, E.T. (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 54–9. PubMed ID #11752404. |
| Bacillus subtilis | Yes | Yes | Follow the standard protocol for bacteria in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resources: Kobs, G. (1998) Promega Notes 68, 28–31. Colombo, M.L. et al. (2004) Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48, 484–90. PubMed ID #14742199. |
| Vibrio vulnificus | Yes | Chen, Y.C. et al. (2004) Infect. Immun. 72, 629–36. PubMed ID #14742502. | |
| Salmonella enterica | Yes | Kelly, A. et al. (2004) Microbiology 150, 2037–53. PubMed ID #15256548. Klein, J.R., Fahlen, T.F. and Jones, B.D. (2000) Infect. Immun. 68, 3368–76. PubMed ID #10816487. | |
| Streptomyces coelicolor | Yes | The biomass from pregerminated Streptomycetes coelicolor spores was collected, frozen in liquid nitrogen and crushed by mortar and pestle. The resulting powder was processed to extract RNA using the TRIzol® reagent, and the aqueous phase was treated with DNase I. SV RNA Dilution Buffer (375µl) was added to the nucleic acid solution, and samples were mixed and centrifuged. The resulting supernatant was mixed with 250µl of cold 96% ethanol, loaded on an SV spin column and centrifuged for 1 minute. The column was then processed as described in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Van Keulen G. et al. (2004) J. Microbiol. Methods 58, 139–42. PubMed ID #15177913. | |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | Yes | Lee, M.K. et al. (2003) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 4648–57. PubMed ID #12902253. | |
| Alteromonas | Yes | Orikoshi, H. et al. (2003) J. Bacteriol. 185, 1153–60. PubMed ID #12562783. Tsujibo, H. et al. (2000) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 3778–83. PubMed ID #10966390. | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Yes | After resuspension in a lysis buffer (50mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 150mM NaCl), the cell pellet was subjected to French press, and 100μl aliquots were processed with the SV Total RNA Isolation System as directed by the manufacturer. Cambronne, E.D. and Schneewind, O. (2002) J. Bacteriol. 184, 5880–93. PubMed ID #12374821. | |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Yes | Brown, J.S. et al. (2002) Infect. Immun. 70, 4389–98. PubMed ID #12117949. | |
| Mycobacterium smegmatis | Yes | Milano, A. et al. (2001) J. Bacteriol. 183, 6801–6. PubMed ID #11698368. | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Yes | Yigit, H. et al. (2001) Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45, 1151–61. PubMed ID #11257029. | |
| Rhizobium leguminosarum | Yes | Lee, H.Y., An, J.H. and Kim, Y.S. (2000) Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 7224–9. PubMed ID #111064359. | |
| Pseudomonas putida | Yes | Cowles, C.E., Nichols, N.N. and Harwood, C.S. (2000) J. Bacteriol. 182, 6339–46. PubMed ID #11053377. Grimm, A.C. and Harwood, C.S. (1999) J. Bacteriol. 181, 3310–6. PubMed ID #10322041. | |
| Rhodopseudomonas palustris | Yes | Pelletier, D.A. and Harwood, C.S. (2000) J. Bacteriol. 182, 2753–60. PubMed ID #107815431. | |
| Neiserria meningitidis | Yes | Deghmane, A.E. et al. (2000) EMBO J. 19, 1068–78. PubMed ID #106989471. | |
| Lactobacillus helveticus | Yes | Pederson, J.A. et al. (1999) J. Bacteriol. 181, 4592–7. PubMed ID #10419958. | |
| Simkania negevensis ZT | Yes | Everett, K.D. et al. (1999) J. Bacteriol. 181, 4734–40. PubMed ID #10438738. | |
| Chlamydia trachomatis | Yes | Everett, K.D. et al. (1999) J. Bacteriol. 181, 4734–40. PubMed ID #10438738. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Yes | A protocol is provided in the SV Total RNA Isolation System Technical Manual #TM048. Additional resource: Kobs, G. (1998) Promega Notes 68, 28–31. | |
| Gigaspora margarita | Yes | Lanfranco, L. et al. (2002) Plant Physiol. 130, 58–67. PubMed ID #12226486. | |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | Yes | Coombs, G.H. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 5249–56. PubMed ID #14630923. | |
| Pacific oyster larvae | Yes | Steele, S. and Thorndyke, M. (1999) Promega Notes 71, 2–4. | |
| Cartilaginous fish brain | Yes | Pederson, J.A. et al. (1999) J. Bacteriol. 181, 4592–7. PubMed ID #10419958. | |
| Zebrafish gut | Yes | Crosnier, C. et al. (2005) Development 132, 1093–104. PubMed ID #15689380. | |
| Drosophila larva tissue | Yes | Petryk, A. et al. (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 13773–8. PubMed ID #14610274. | |
| Frog liver | Yes | Saeed-Kothe, A. and Powers-Lee, S.G. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 26722–6. PubMed ID #12738780. | |
| Frog gonads and mesonephroi | Yes | Ogata, M. et al. (2003) Genetics, 164, 613–20. PubMed ID #12807781. | |
| Chicken embryonic heart, brain and skeletal muscle | Yes | Agarkova, I. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10256–64. PubMed ID #10744711. | |
| Venom sacs and glands from Naja Atra (Asian cobra) | Yes | Lou, X. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 39094–104. PubMed ID #15252034. | |
| Microcystis aeruginosa | Yes | Kaebernick, M. et al. (2002) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 449–55. PubMed ID #11823177. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| In vitro transcribed RNA | Yes | M. Raynor, J.O. and Butler, K.D. (2004) Promega Notes 86, 15–7. | |
| Human immunodeficiency virus | Yes | Personal communication. Contact Promega Technical Services for more information. | |
| RNA from soil | Yes | Personal communication. Contact Promega Technical Services for more information. |
Protocols
Complete Protocol
Quick Protocol
What’s in the box?
| Item - Catalog number: Z3101 | Part # | Size | Available Separately |
| Collection Tubes | A130E | 2 × 5/pk | |
| Nuclease-Free Water | P119A | 1 × 1,250μl | View Product |
| Elution Tubes | Z200A | 2 × 5/pk | |
| RNA Lysis Buffer (RLA) | Z305B | 1 × 10ml | View Product |
| RNA Dilution Buffer (RDA) | Z306B | 1 × 4ml | |
| RNA Wash Solution (RWA) | Z309B | 1 × 11.8ml | View Product |
| DNase Stop Solution (DSA) | Z312A | 1 × 5.3ml | |
| Yellow Core Buffer | Z317A | 1 × 2.5ml | |
| MnCl2, 0.09M | Z318A | 1 × 250μl | |
| DNase I (lyophilized) | Z358B | 1 × 1 vial | |
| Spin Columns | Z503B | 2 × 5/pk | |
| Beta-Mercaptoethanol | Z559A | 1 × 900μl |
SDS
 Download SDS
Download SDS
Use Restrictions
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
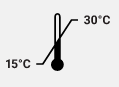
Storage Conditions
What’s in the box?
| Item - Catalog number: Z3100 | Part # | Size | Available Separately |
| Collection Tubes | A130D | 2 × 25/pk | |
| Nuclease-Free Water | P119E | 1 × 13ml | View Product |
| Elution Tubes | Z200B | 2 × 25/pk | |
| RNA Lysis Buffer (RLA) | Z3051 | 1 × 50ml | View Product |
| RNA Dilution Buffer (RDA) | Z306A | 1 × 20ml | |
| RNA Wash Solution (RWA) | Z3091 | 1 × 58.8ml | |
| DNase Stop Solution (DSA) | Z312A | 1 × 5.3ml | |
| Yellow Core Buffer | Z317A | 1 × 2.5ml | |
| MnCl2, 0.09M | Z318A | 1 × 250μl | |
| DNase I (lyophilized) | Z358A | 1 × 1 vial | |
| Spin Columns | Z503C | 2 × 25/pk | |
| Beta-Mercaptoethanol | Z559A | 1 × 900μl |
SDS
 Download SDS
Download SDS
Use Restrictions
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
Storage Conditions

What’s in the box?
| Item - Catalog number: Z3105 | Part # | Size | Available Separately |
| Collection Tubes | A130A | 5 × 50/pk | |
| Nuclease-Free Water | P119C | 2 × 25ml | View Product |
| Elution Tubes | Z200C | 5 × 50/pk | |
| RNA Lysis Buffer (RLA) | Z305E | 1 × 250ml | View Product |
| RNA Dilution Buffer (RDA) | Z306C | 1 × 96ml | |
| RNA Wash Solution (RWA) | Z309D | 1 × 206ml | View Product |
| DNase Stop Solution | Z312D | 1 × 26.5ml | |
| Yellow Core Buffer | Z317C | 1 × 11ml | |
| MnCl2, 0.09M | Z318B | 2 × 750μl | |
| Spin Columns | Z503D | 5 × 50/pk | |
| Beta-Mercaptoethanol | Z559A | 1 × 900μl |
SDS
 Download SDS
Download SDS
Use Restrictions
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
Storage Conditions