Description
Manual, Solution-Based DNA Extraction Method
Simple Method to Isolate Genomic DNA from Many Sample Types
The Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a simple, solution-based method for isolation of DNA from white blood cells, tissue culture cells, animal tissue, plant tissue, yeast and Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. DNA purified with this system is suitable for a variety of applications, including amplification, digestion with restriction endonucleases and membrane hybridizations (e.g., Southern and dot/slot blots).
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Blood and blood cells | |||
| Human whole blood | Yes | Yes | Protocols are provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050 for samples of up to 10ml blood or in 96-well plates ("Isolating Genomic DNA from Whole Blood" sections). The protocol works with the following anticoagulants: EDTA, heparin and citrate. Reference:Rizzo, W.B., Carney, G. and Lin, Z. (1999) Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65, 1547–60. PubMed ID #10577908 |
| Mouse whole blood | Yes | A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050. | |
| Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells | Yes | Tan, A. et al. (2006) Clin. Chem. 52, 2250–7. PubMed ID #17040960 | |
| Bovine whole blood | Yes | Walker, J.A. et al. (2003) Anal. Biochem. 316, 259–69. PubMed ID #12711348 | |
| Horse whole blood | Yes | Walker, J.A. et al. (2003) Anal. Biochem. 316, 259–69. PubMed ID #12711348 | |
| Sheep whole blood | Yes | Walker, J.A. et al. (2003) Anal. Biochem. 316, 259–69. PubMed ID #12711348 | |
| Antelope whole blood | Yes | Walker, J.A. et al. (2003) Anal. Biochem. 316, 259–69. PubMed ID #12711348 | |
| Dog whole blood | Yes | Walker, J.A. et al. (2003) Anal. Biochem. 316, 259–69. PubMed ID #12711348 | |
| Cat whole blood | Yes | Walker, J.A. et al.(2003) Anal. Biochem. 316, 259–69. PubMed ID #12711348 | |
| Rabbit whole blood | Yes | Walker, J.A. et al. (2003) Anal. Biochem. 316, 259–69. PubMed ID #12711348 |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Mammalian tissues | |||
| Mouse liver | Yes | Yes | Tissue needs to be homogenized prior to isolation. A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Tissue Culture Cells and Animal Tissue" section. Reference:Barazzoni, R. et al. (2005) Endocrinology 146, 2098–106. PubMed ID #15618355. |
| Mouse tail | Yes | Yes | Tail needs to be treated with proteinase K before purification. A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Tissue Culture Cells and Animal Tissue" section. Reference:Nielsen, J.V. et al. (2007) Development 134, 1133–40. PubMed ID #17301088. |
| Mouse brain | Yes | Sinz, E.H. et al. (1999) J. Clin. Invest. 104, 647–56. PubMed ID #10487779. | |
| Mouse Lymphoma | Yes | Yu, Z. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66, 755–62. PubMed ID #16424006. | |
| Rat skeletal muscle, liver and heart | Yes | Barazzoni, R. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 3343–7. PubMed ID #10652323. | |
| Human bone marrow aspirate | Yes | Yu, Z. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66, 755–62. PubMed ID #16424006. | |
| Human liver and testicle | Yes | Maduro, M.R. et al. (2003) Mol. Hum. Reprod. 9, 61–8. PubMed ID #12569174. | |
| Human colon | Yes | Tost, J. et al. (2003) Nucleic Acids Res. 31, e50. PubMed ID #12711695. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Plant tissues | |||
| Tomato leaf | Yes | Leaf needs to be frozen in liquid nitrogen and ground with a mortar and pestle prior to adding lysis buffer. A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Plant Tissue" section. | |
| Arabidopsis | Yes | Vorwerk, S. (2001) Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit and the isolation of plant genomic DNA. eNotes | |
| Maize | Yes | Vorwerk, S. (2001) Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit and the isolation of plant genomic DNA. eNotes | |
| Lemna minor (aquatic plant) | Yes | Stout, L.M. and Nüsslein, K. (2005) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 2484–92. PubMed ID #15870338. | |
| Medicago truncatula | Yes | Total DNA was isolated from roots, which may include various mycorrhizal fungi. Kosuta, S. et al. (2003) Plant Physiol. 131, 952–62. PubMed ID #12644648. | |
| Tetrahymena thermophila | Yes | Followed plant DNA protocol ("Isolating Genomic DNA from Plant Tissue"), but skipped freezing in liquid nitrogen and grinding with a mortar and pestle. Jacobs, M.E. et al. (2006) Eukaryot. Cell 5, 1990–2000. PubMed ID #17012537. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Cultured cells (Established cell lines are not listed.) | Yes | Yes | A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Tissue Culture Cells and Animal Tissue" section. Reference:Zhang, S. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66, 8847–57. PubMed ID #16951202. |
| Drosophila D.Mel-2 embryonic cells | Yes | Roberti, M. et al. (2006) Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 2109–16. PubMed ID #16648357. | |
| Mouse embryonic stem cells | Yes | Oka, M. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281, 9901–8. PubMed ID #16439359. | |
| Monkey primary fibroblasts, virus-infected | Yes | Cells were lysed using 300 µl of Nuclei Lysis Solution with proteinase K and incubating overnight at 37°C. Mansfield, K.G. et al. (1999) J. Virol. 73, 10320–8. PubMed ID #10559350. | |
| Vero cells infected with HSV-1 | Yes | Both viral and genomic DNA were isolated. Bower, J.R. et al. (1999) J. Virol. 73, 3843–53. PubMed ID #10196279. | |
| CD45RA+ T cells from cord blood | Yes | Samples of 2–4 × 106 cells were pelleted, washed with PBS, snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and frozen at –70°C prior to using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit. Soares et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 161, 5909–17. PubMed ID #9834071. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Bacteria – Gram Negative | |||
| Enterobacter cloacae | Yes | A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria" section. | |
| Escherichia coli | Yes | Yes | A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria" section. Reference: Zheng, W. et al. (2001) EMBO J. 20, 1164–72. PubMed ID #11230139. |
| Nitrobacter winogradskyi | Yes | Starkenburg, S.R. et al. (2006) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 2050–63. PubMed ID #16517654. | |
| Yersinia pestis | Yes | Flashner, Y. et al. (2004) Infect. Immun. 72, 908–15. PubMed ID #14742535. | |
| Burkholderia species | Yes | Moore, R.A. et al. (2004) Infect. Immun. 72, 4172–87. PubMed ID #15213162. | |
| Salmonella enterica | Yes | Nair, S. et al. (2004) J. Bacteriol. 186, 3214–23. PubMed ID #15126484. | |
| Field bacteria samples, non-Agrobacterium | Yes | Weller, S.A. et al. (2004) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 2779–85. PubMed ID #15128532. | |
| Haemophilus influenzae | Yes | Ottemann, K.M. and Lowenthal, A.C. (2002) Infect. Immun. 70, 1984–90. PubMed ID #11895962. | |
| Bordetella bronchiseptica | Yes | Brockmeier, S.L. et al. (2002) Infect. Immun. 70, 481–90. PubMed ID #11796573. | |
| Leptospira kirschneri | Yes | Matsunaga, J. et al. (2002) Infect. Immun. 70, 323–34. PubMed ID #11748198. | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Yes | Yigit, H. et al. (2001) Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45, 1151–61. PubMed ID #11257029. | |
| Marine Geobacteraceae | Yes | Bacteria colonizing energy-harvesting anodes were scraped off, organically extracted and purified using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit. Bond, D.R. et al. (2002) Science 295, 483–5. PubMed ID #11799240. | |
| Serratia marcescens | Yes | Peccia, J. and Hernandez, M. (2001) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 4225–32. PubMed ID #11526027. | |
| Borrelia burgdorferi | Yes | Chaconas, G. et al. (2001) EMBO J. 20, 3229–37. PubMed ID #11406599. | |
| Campylobacter jejuni | Yes | Dorrell, N. et al.(2001) Genome Res. 11, 1706–15. PubMed ID #11591647. | |
| Desulfovibrio desulfuricans | Yes | Rapp-Giles, B.J. et al. (2000) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 671–7. PubMed ID #10653734. | |
| Vibrio cholerae | Yes | Stine, O.C. et al. (2000) Infect. Immun. 68, 7180–5. PubMed ID #11083852. | |
| Vibrio harveyi | Yes | Zhou, W. et al. (1999) Biochemistry 38, 16246–52. PubMed ID #10587447. | |
| Paracoccus denitrificans | Yes | Shearer, N. et al. (1999) J. Bacteriol. 181, 6907–13. PubMed ID #10559155. | |
| Campylobacter species | Yes | Before genomic DNA isolation, the bacteria were washed in TE buffer and resuspended in 1ml of TE buffer at ~1 × 109 cells/ml. Duim, B. et al. (1999) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 2369–75. PubMed ID #10347015. | |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis | Yes | Jiang, S.C. et al. (1998) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 535–42. PubMed ID #9464390. | |
| Flavobacterium species | Yes | Jiang, S.C. et al. (1998) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 535–42. PubMed ID #9464390. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Bacteria – Gram Positive | |||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Yes | Yes | Cells need to be treated with a lytic enzyme before lysis buffer addition. A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria" section. Reference: Vandecasteele, S.J. et al. (2001) J. Bacteriol. 183, 7094–101. PubMed ID #11717267. |
| Bacillus anthracis | Yes | Pomerantsev, A.P. et al. (2006) Infect. Immun. 74, 682–93. PubMed ID #16369025. | |
| Bacillus cereus | Yes | van Schaik, W. et al. (2004) J. Bacteriol. 186, 316–25. PubMed ID #14702299. | |
| Bacillus subtilis | Yes | Ben-Yehuda, S. and Losick, R. (2002) Cell 109, 257–66. PubMed ID #12007411. | |
| Staphylococcus, 12 strains | Yes | Li, Y. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 3481–6. PubMed ID #12904342. | |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | Yes | Li, Y. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 3481–6. PubMed ID #12904342. | |
| Actinomyces naeslundii | Yes | Li, Y. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 3481–6. PubMed ID #12904342. | |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Yes | Brown, J.S. et al. (2002) Infect. Immun. 70, 4389–98. PubMed ID #12117949. | |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Yes | Yes | Cells need to be treated with a lytic enzyme before lysis buffer addition. A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria" section. Reference: Vandecasteele, S.J. et al. (2001) J. Bacteriol. 183, 7094–101. PubMed ID #11717267. |
| Bacillus anthracis | Yes | Pomerantsev, A.P. et al. (2006) Infect. Immun. 74, 682–93. PubMed ID #16369025. | |
| Bacillus cereus | Yes | van Schaik, W. et al. (2004) J. Bacteriol. 186, 316–25. PubMed ID #14702299. | |
| Bacillus subtilis | Yes | Ben-Yehuda, S. and Losick, R. (2002) Cell 109, 257–66. PubMed ID #12007411. | |
| Staphylococcus, 12 strains | Yes | Li, Y. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 3481–6. PubMed ID #12904342. | |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | Yes | Li, Y. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 3481–6. PubMed ID #12904342. | |
| Actinomyces naeslundii | Yes | Li, Y. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 3481–6. PubMed ID #12904342. | |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Yes | Brown, J.S. et al. (2002) Infect. Immun. 70, 4389–98. PubMed ID #12117949. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Bacteria – Other Bacteria | |||
| Treponema species | Yes | Cells were grown, centrifuged and washed three times with PBS. Protocol for Gram negative bacteria ("Isolating Genomic DNA from Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria") was then followed. Additional Resource: Greene, S.R. and Stamm, L.V. (1998) Promega Notes 68, 30. | |
| Methanococcus jannaschii | Yes | Löwe, J. and Amos, L.A. (1998) Nature 391, 203–6. PubMed ID #9428770. | |
| Methanosarcina mazei | Yes | Lange, M. et al. (2000) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 1796–1800. PubMed ID #10788341. | |
| Mycoplasma hyorhinis | Yes | Cells were collected and lysed in 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 45mM Tris (pH 8.0) and 9mM EDTA for 10 minutes at 50°C, then incubated for 10 minutes at 37°C. The Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit was subsequently used for genomic DNA extraction. Citti, C. et al. (2000) J. Bacteriol. 182, 1356–63. PubMed ID #10671459. | |
| Mycobacterium parafortuitum | Yes | Cells were treated with proteinase K and lysozyme for 1 hour, centrifuged and resuspended in Nuclei Lysis Solution. Glass beads were added, the glass bead-cell lysate shaken for 5 minutes, incubated at 65°C for 1 hour and the glass bead-lysate shaken again for 3 minutes. The protocol then followed the bacterial method of the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit ("Isolating Genomic DNA from Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria"). Peccia, J. and Hernandez, M. (2001) Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 4225–32. PubMed ID #11526027. | |
| Intestinal microflora | Yes | Chicken intestines were removed and the contents of each segment (duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and cecum) were inverted into a sterile 15ml tube containing 9ml of sterile PBS. After adding 4mm glass beads, the samples were vortexed for 3 minutes, and the debris was removed by centrifuging at 700 × g for 1 minute. The supernatant was collected and centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 5 minutes. The pellet was washed twice with PBS and stored at –20°C until DNA extraction. This frozen pellet was resuspended in EDTA and treated with lysozyme (at a final concentration of 10mg/ml) for 45 minutes at 37°C. The bacterial genomic DNA was isolated with the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit. Amit-Romach, E., Sklan, D. and Uni, Z. (2004) Poult. Sci. 83, 1093–98. PubMed ID #15285498 |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Yeast- | |||
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Yes | Yes | Yeast need to be treated with lyticase prior to adding lysis buffer. A protocol is provided in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Yeast" section. Reference: Soteropoulos, P. and Perlin, D.S. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 26426–31. PubMed ID #9756876. |
| Candida species, various | Yes | Yeast cells were incubated for 1 hour at 37°C with 1 M sorbitol, 0.1 M EDTA, 0.1% (w/v) zymolyase-100T (Seikaguku Corp.), and 1% (v/v) 2-mercaptoethanol adjusted to pH 7.5. Chromosomal DNA was then isolated using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit. Park, S. et al.(2000) J. Clin. Microbiol. 38, 2829–36. PubMed ID #10921935. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Fungus- | |||
| Madurella mycetomatis | Yes | Mycelia were sonicated and ground in liquid nitrogen before the addition of Nuclei Lysis Solution. Ahmed, A. et al. (2003) J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 4537–41. PubMed ID #14532179. | |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | Yes | Cells were filtered through a 0.2µm SFCA filter, frozen on dry ice, then ground with a mortar and pestle. The ground cells were incubated in Nuclei Lysis Solution at 37°C for 1 hour before purifying with the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit," Isolating Genomic DNA from Tissue Culture Cells and Animal Tissue" section. Burghoorn, H.P. et al. (2002) Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46, 615–24. PubMed ID #11850239. | |
| Nectria haematococca | Yes | Mycelia were ground in liquid nitrogen and lyophilized before lysing in a modified lysis buffer consisting of 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 50 mM EDTA (pH 8.0), 3% SDS and 1% mercaptoethanol. Wu, Q. et al. (1998) Mol. Biol. Cell 9, 89–101. PubMed ID #9436993. | |
| Pneumocystis carinii | Yes | Sputum samples were dispensed into ~1ml aliquots and centrifuged at 14,000 × g for 5–7 minutes. The cell pellet was resuspended in 1 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (0.01M, pH 7.2) containing 1mM EDTA (PBS-EDTA), washed twice in PBS-EDTA, centrifuged and stored at –80°C for later DNA extraction. DNA was prepared using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Whole Blood " section. Beard, C.B. et al. (2000) Emerg. Infect. Dis. 6, 265–72. PubMed ID #10827116. |
| Sample Type | Promega | External | Comments |
| Other Organisms and Tissues - | |||
| Single flour beetles (Tribolium castaneum) | Yes | Lorenzen, M.D. et al. (2002) Genetics 160, 225–34. PubMed ID #11805058. | |
| Drosophila, adult fly | Yes | To prepare genomic DNA from adult D. virilis and D. melanogaster, 100 adult flies were homogenized and the DNA purified using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit. Hanrahan, C.J. et al. (2000) Genetics 155, 1149–60. PubMed ID #10880477. | |
| Frog Skin | Yes | Skin biopsies from Amphibiocystidium ranae (10µm sections) were deparaffinized twice in xylene and centrifuged at high speed. The tissue pellet was washed with 95% and 70% ethanol, then dried, and the genomic DNA was extracted using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit. Pereira, C.N. et al. (2005) J. Clin. Microbiol. 43, 192–8. PubMed ID #15634971. | |
| Cichlid fin and whole fish | Yes | Genomic DNA was isolated from 1–2 mm2 ethanol-preserved Neolamprologus pulcher finclip samples or whole offspring using the Wizard® Genomic DNA Isolation Kit, "Isolating Genomic DNA from Tissue Culture Cells and Animal Tissue" section, with small modifications (not listed). Heg, D. et al. (2006) Behav. Ecol. 17, 419–29. | |
| Plasmodium vivax | Yes | Researchers used a modified animal tissue/tail snip protocol. Sawabe, T and Ikeda, T. (2005) Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides high-quality genomic DNA template for molecular phylogenetic studies on Copepod crustaceans. eNotes | |
| Plasmodium vivax | Yes | To isolate the parasite from whole blood, a modified protocol was used.Centrifuge 15ml vials containing infected sodium-citrate whole blood at 3,000rpm for 10 minutes.Extract serum and leukocytes with 5ml pipettes.Dilute erythrocytes in 7 volumes of 0.15% saponin.Incubate at 37°C for 1 hour.Centrifuge at 3,000rpm for 40 minutes.Discard supernatant, taking care not to disturb the parasite pellet.Resuspend the pellet in 15ml of 1X PBS and centrifuge at 3,000rpm for 10 minutes. Discard the supernatant, and repeat the procedure twice.Start with the Nuclei Lysis Solution addition step in the "Isolating Genomic DNA from Whole Blood" section of the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050. (Personal communication) | |
| Amoeba | Yes | Trophozoites of clone A of Entamoeba histolytica (strain HM1:IMSS) were "axenically cultured" in TYI-S33 medium. Trophozoites (3 × 106) were processed as described in the Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual #TM050, following the protocol for isolation of genomic DNA from tissue culture cells ("Isolating Genomic DNA from Tissue Culture Cells and Animal Tissue" section). DNA pellet was dissolved with 50µl of DNA rehydration solution and incubated overnight at 4°C. Yield: 2.5µg per 3 × 106 trophozoites. Purity A260/280: 1.8. (Personal communication) |
Protocols
Complete Protocol
Wizard® Genomic DNA Purification Kit Technical Manual
Quick Protocol
Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit Quick Protocol FB022
What’s in the box?
100 isolations × 300μl
| Item - Catalog number: A1120 | Part # | Size | Available Separately |
| Cell Lysis Solution | A793A | 1 × 100ml | View Product |
| Nuclei Lysis Solution | A7941 | 1 × 50ml | View Product |
| Protein Precipitation Solution | A795A | 1 × 25ml | View Product |
| DNA Rehydration Solution | A796A | 1 × 50ml | View Product |
| RNase A Solution | A797A | 1 × 250μl | View Product |
SDS
 Download SDS
Download SDS
Use Restrictions
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
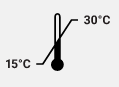
Storage Conditions
What’s in the box?
500 isolations × 300μl
| Item - Catalog number: A1125 | Part # | Size | Available Separately |
| Cell Lysis Solution | A793A | 5 × 100ml | View Product |
| Nuclei Lysis Solution | A7941 | 5 × 50ml | View Product |
| Protein Precipitation Solution | A795A | 5 × 25ml | View Product |
| DNA Rehydration Solution | A796A | 2 × 50ml | View Product |
| RNase A Solution | A797A | 5 × 250μl | View Product |
SDS
 Download SDS
Download SDS
Use Restrictions
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
Storage Conditions

What’s in the box?
100 isolations × 10ml
| Item - Catalog number: A1620 | Part # | Size |
| Cell Lysis Solution (Genomic Purification) | A7933 | 3 × 1 liter |
| Nuclei Lysis Solution | A7943 | 1 × 1 liter |
| Protein Precipitation Solution | A7953 | 1 × 350ml |
| DNA Rehydration Solution | A7963 | 3 × 50ml |
SDS
 Download SDS
Download SDS
Use Restrictions
For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic Procedures.
Storage Conditions