Description
TraPR (Trans-kingdom, rapid, affordable Purification of RISCs) presents a gel- and bias-free, column-based method for isolation of functional small RNAs from RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs) of all organisms. Within 15 minutes, TraPR enables purification of RISC fractions even from challenging or inconsistent samples, cell types, tissues, and bio-fluids. The TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit generates high-quality sRNA preparations suitable for Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) applications and thus provides a highly reproducible, time-saving method that outperforms all current gold-standard procedures for sRNA profiling.
Features and Application:
- Next Generation Sequencing (bundle with Lexogen’s Small RNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina, Cat. No. 135)
- Analysis of functional small RNAs
- Expression and sequence analysis of piRNAs, siRNAs, miRNAs, and scnRNAs
- Discovery of novel biomarkers
- Analysis of RISCs
Kit Content:
- Buffers and TraPR columns
128 (TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit),
135 (Small RNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina with TraPR)
TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit
TraPR (Trans-kingdom, rapid, affordable Purification of RISCs) presents a gel- and bias-free, column-based method for isolation of functional small RNAs from RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs) of all organisms. Within 15 minutes, TraPR enables purification of RISC fractions even from challenging or inconsistent samples, cell types, tissues, and bio-fluids. The TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit generates high-quality sRNA preparations suitable for Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) applications and thus provides a highly reproducible, time-saving method that outperforms all current gold-standard procedures for sRNA profiling.
TraPR Eliminates the Need for Gel Extraction of sRNAs
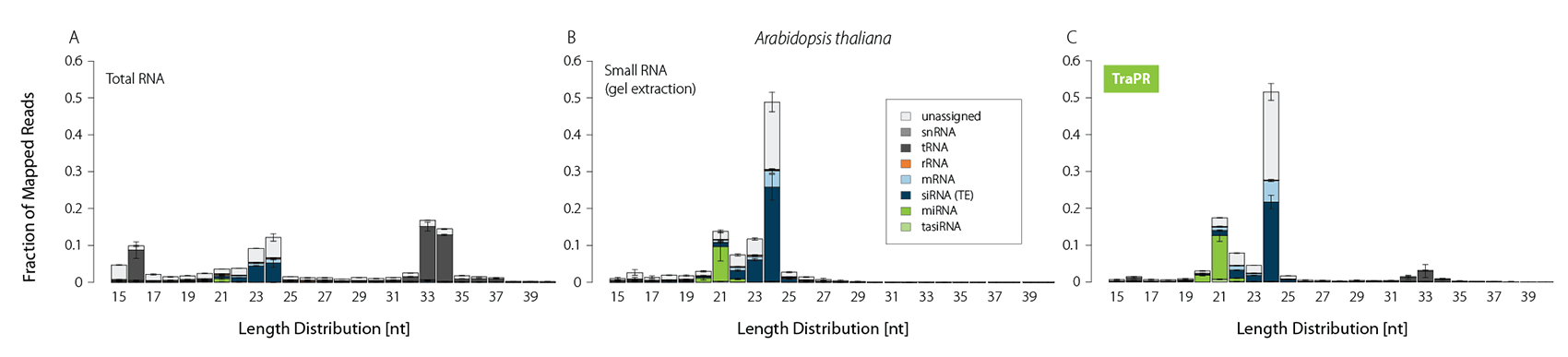
Typically, sRNA-Seq libraries from total RNA contain only a minor fraction of reads corresponding to functional sRNAs (Fig. 1A). Thus, size selection methods such as gel extraction are commonly applied to increase the share of sRNA-mapping reads (Fig. 1B). TraPR replaces these lengthy and error-prone gel extractions with quick and easy column purifications (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1 | TraPR enriches functional sRNA without the need for gel extraction. Size distribution and biotypes of mapped reads from NGS libraries prepared from A) Total RNA (TRIzol extraction), B) gel-purified, or C) TraPR-isolated sRNA from Arabidopsis thaliana. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
TraPR is Universal and Species-Independent
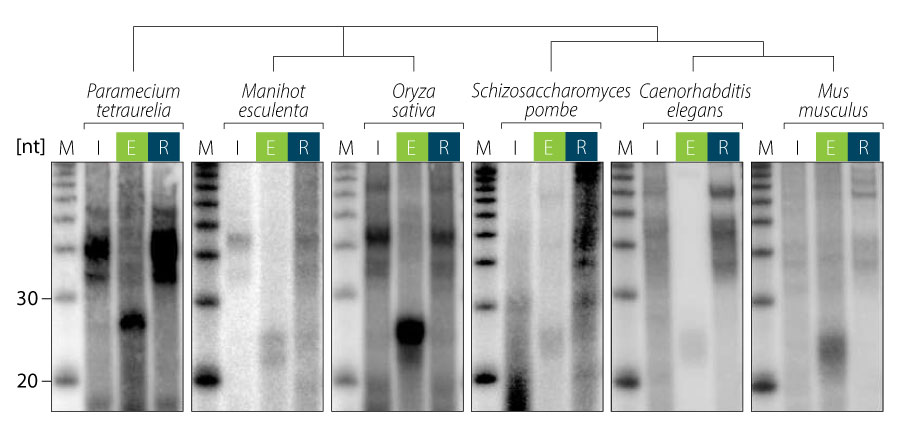
The TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit easily isolates all RISC-associated sRNAs found in any organism, tissue, cell type, or bio-fluid. No previous characterization or knowledge of the organism of interest is required (Fig. 2).
Figure 2 | TraPR isolation of RISC-associated sRNAs exemplified for ciliate, plant, yeast, nematodes, and mammalian samples. RNA was extracted from input (I), TraPR eluate (E), and column-retained (R) fractions, radiolabeled and analyzed by gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
TraPR Isolates High-Quality sRNA from Challenging Samples
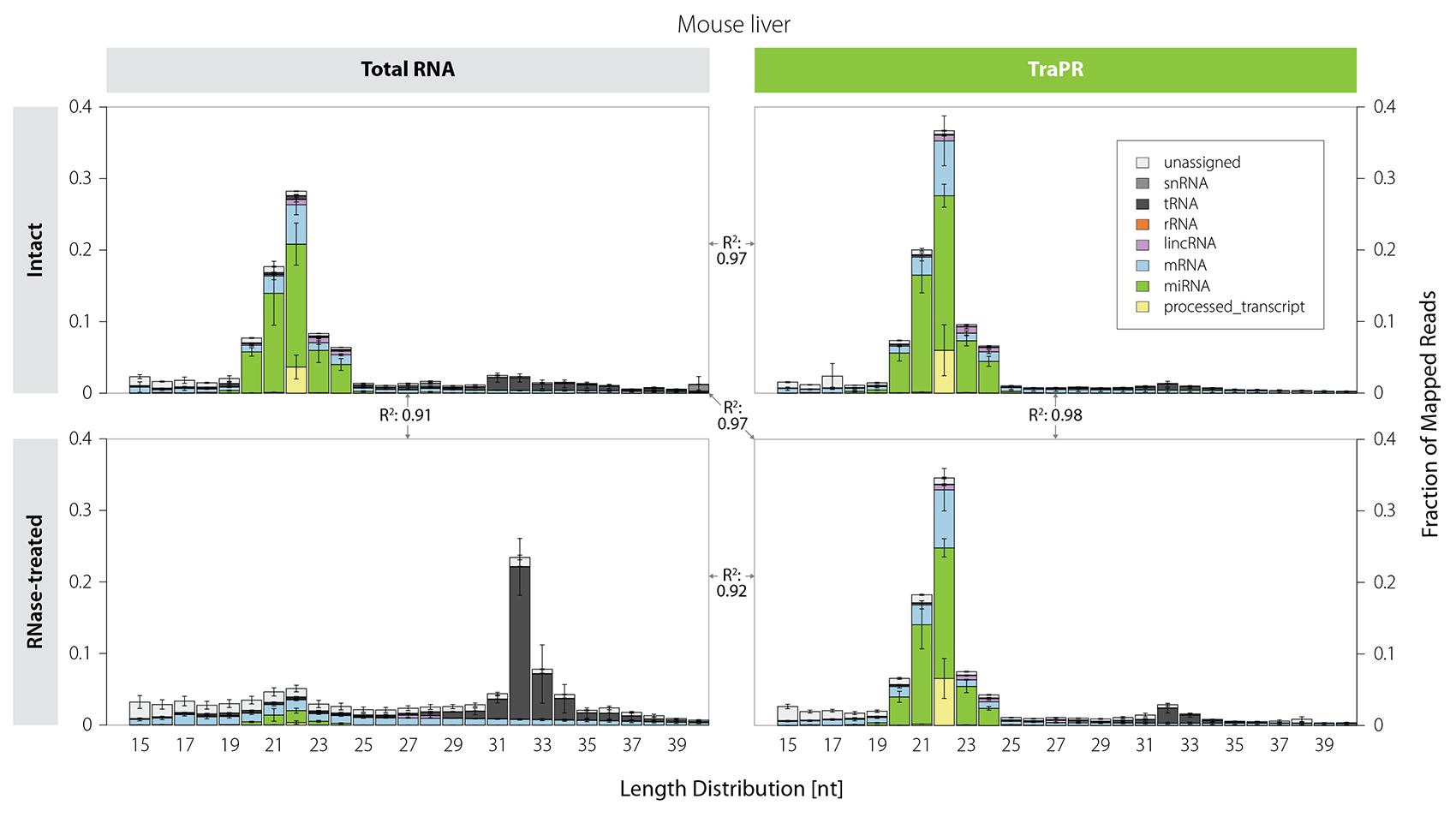
Size-based selection does not distinguish between functional sRNAs and short RNA fragments originating from degradation. Thus, sRNA library preps from samples that are prone to RNA degradation are often heavily contaminated with tRNA-, mRNA-, and rRNA-derived fragments (Fig. 3, left). In contrast, TraPR isolation preserves the sRNA size distribution even for RNA-degraded samples (Fig. 3, right).
Figure 3 | TraPR enables clean isolation of high-quality sRNA from RNA-degraded samples. Mus musculus liver lysates were treated for 30 minutes with RNase T1 to simulate RNA degradation. Size distribution and biotypes of mapped reads from NGS libraries prepared from Total RNA (TRIzol extraction) or TraPR-isolated sRNA from intact or RNase-treated samples. The R² values between the panels refer to the respective miRNA read count correlations. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
TraPR Enriches Low-Abundant miRNAs e.g. from Plasma
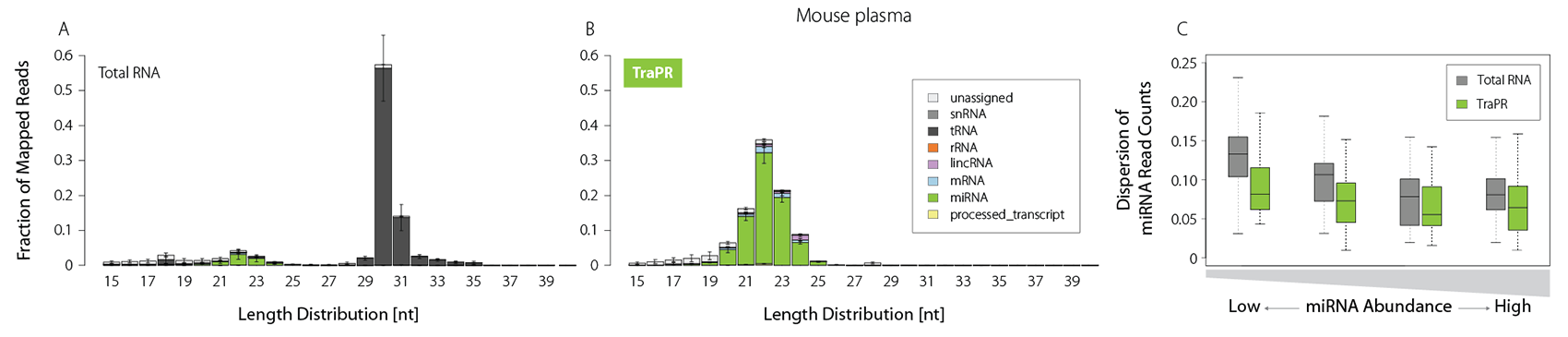
Plasma is of growing interest for biomarker discovery, but it is often prone to RNA degradation and/or contains only minute amounts of sRNAs. TraPR enriches sRNAs even from such challenging samples by one order of magnitude (Fig. 4A and B).
It further reduces the read count dispersion particularly for low-abundant miRNAs, enabling precise quantification (Fig. 4C). Small RNA isolation from liquid samples thereby becomes easily accessible, and TraPR is perfectly suited for biomarker discovery applications.
Figure 4 | TraPR robustly detects low-abundant sRNA from plasma samples. Total RNA (TRIzol) or TraPR-isolated RNA from 150 µl Mus musculus plasma were converted to NGS libraries and sequenced. A) and B) Size distribution and biotypes of mapped reads. C) Box plot representation of miRNA NGS read count dispersion, grouped by miRNA abundance. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
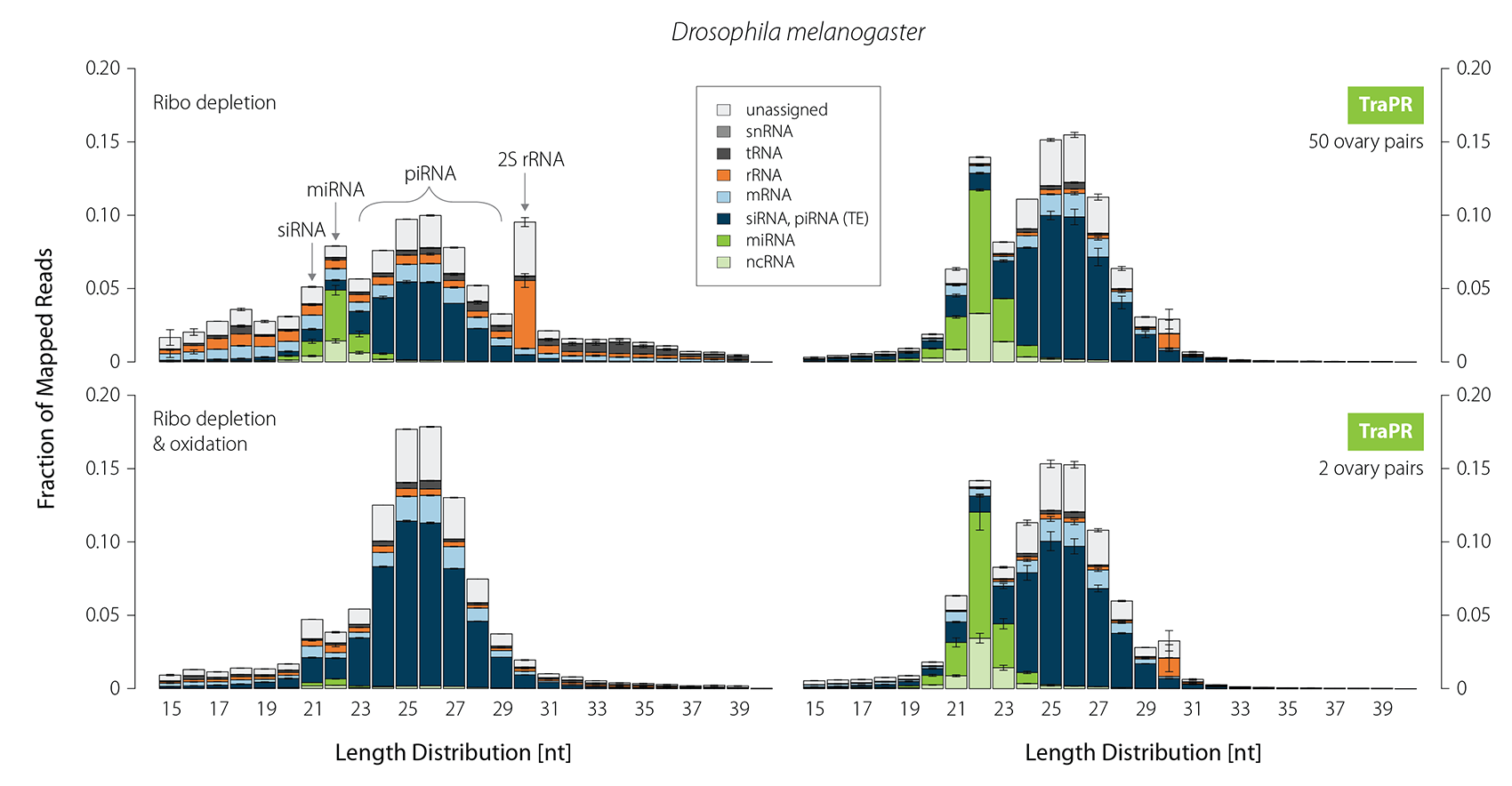
TraPR Works Consistently Over a Large Input Range and Eliminates the Need for rRNA Depletion
Small RNA profiling of certain tissue types requires extensive and laborious sample preparation. In Drosophila ovaries, for instance, the 30 nt long 2S rRNA is highly abundant. Therefore, a typical piRNA library generation from fly gonads is a two- to three-day process of gel-based size selection, customized depletion, and oxidation of 2S rRNA and other abundant RNA fragments. While oxidation effectively removes contaminants, it also eliminates the majority of miRNAs. In contrast, sRNA isolation using TraPR fully preserves miRNAs, siRNAs, and piRNAs without requiring depletion of contaminating non-regulatory RNAs (Fig. 5). Furthermore, TraPR can be used over a broad input range starting from as little as two ovary pairs.
Figure 5 | TraPR robustly enriches all classes of sRNAs while eliminating 2S rRNA from Drosophila ovaries. Size distribution and biotypes of mapped reads from NGS libraries. 10 µg of total RNA were used for gel selection followed by ribo-depletion (+/- oxidation). For TraPR-based isolation only two or 50 ovary pairs were used as input. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
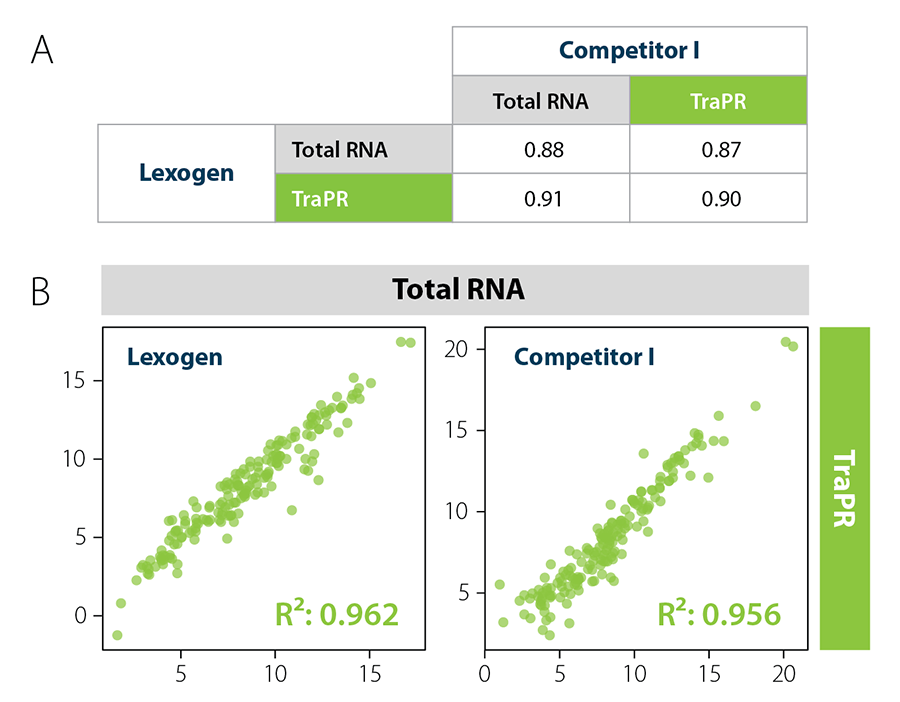
Combining TraPR With Lexogen’s Small RNA Library Prep Kit
The TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit is suitable for various downstream applications such as qRT-PCR, low molecular weight RNA blotting, sRNA cloning, and NGS sample preparation. TraPR is fully compatible with Small RNA-Seq library preparation protocols using adaptor ligation including Lexogen’s Small RNA Library Preparation Kit (Cat. No. 052, Fig. 6). For convenience, a bundled option is also available (Cat. No. 135).
Figure 6 | Lexogen’s Small RNA Library Prep Kit yields highest quality results with TraPR. Correlation analysis of miRNAs from murine plasma. A) R² values for miRNA correlation analysis show compatibility of TraPR with Small RNA-Seq Library Preparation Kits from Lexogen and Competitor I. B) Correlation plots of miRNA read counts from Total RNA (TRIzol extraction) vs. TraPR-isolated sRNAs libraries generated with Small RNA-Seq Library Preparation Kits from Lexogen or Competitor I. Adapted from Grentzinger et al., 2020.
Testimonials
“Overall, TraPR was our best, fastest, and the most economic way to investigate siRNA sizes in non-sequenced species, i.e. duckweeds.”
“The TraPR kit was very good at efficiently and specifically isolating small RNAs. I used it on Drosophila melanogaster tissues for differential analysis using qRT-PCR. I definitely recommend it.”
“The TraPR column greatly improve my preparation of sRNA libraries, as it speeds up the otherwise more laborious sRNA preparation. Moreover, by using TraPR I could increase the number of samples loaded per lane of the sequencing flow cell, without decreasing the amount of reads per sample.”
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Please find a list of the most frequently asked questions below. If you cannot find the answer to your question here or want to know more about our products, please contact info@gomolecular.pk .
1. How does TraPR achieve species-independent isolation of functional sRNAs?
TraPR relies on the high conservation of AGO proteins structural and biochemical properties to specifically select sRNA-associated AGO ribonucleoprotein complexes.
2. What RNA species does TraPR isolate?
TraPR isolates all functional silencing sRNAs that are associated with AGO proteins, including piRNAs, siRNAs, miRNAs, scnRNAs and RNAi-competent tRNA fragments.
3. In which organisms has TraPR been tested?
TraPR has been successfully tested on A. thaliana, P. tetraurelia, O. sativa, M. esculenta, S. pombe, C. elegans, M. musculus, D. melanogaster and H. sapiens.
4. Do I need any special equipment to use TraPR?
No, the only required piece of equipment is a benchtop centrifuge. For the complete list of user-supplied consumables and equipment, see the TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit User Guide (page 7).
5. Do I need any extra reagents to purify the sRNAs?
Acidic phenol, chloroform, isoamylalcohol, ethanol and isopropanol have to be supplied by the user. We recommend purchasing the phenol solution pH 4.3 e.g. Sigma-Aldrich (P4682-100ML) or VWR (Cat. No. 0981-100ML). For the complete list of user-supplied consumables and equipment, see the TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit User Guide (page 7).
6. Can I use TraPR with low RNA-containing bio-fluids such as plasma?
Yes, TraPR has been successfully used with 150 µL plasma.
7. Can I use TraPR for FFPE samples?
No, only flash frozen or fresh material is suitable for TraPR, because the RISCs have to be in native state. FFPE samples, samples stored in RNAlater, or other denaturing agents are not suitable.
8. Is TraPR-isolated sRNA suitable for high-throughput sequencing?
Yes, TraPR-isolated sRNAs are suitable for all molecular biology and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) applications. For NGS library preparation we recommend using Lexogen’s Small RNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina (Cat. No. 052). For convenience, a bundled version with TraPR is also available (Cat. No. 135).
9. Can I use the purified RISC fraction for downstream biochemical analyses?
Yes, the TraPR elution fraction which contains the purified RISCs can be used for downstream protein biochemistry techniques such as immuno-precipitation, mass spectrometry, immunoblotting, etc.
Downloads
Use for Cat. No.s: 128 (TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit), and 135 (Small RNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina with TraPR)
![]() 128UG242V0100 – User Guide for TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit – release 04.06.2020
128UG242V0100 – User Guide for TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit – release 04.06.2020
![]() 128MS269V0100 – MSDS Information for TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kits – release 04.06.2020
128MS269V0100 – MSDS Information for TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kits – release 04.06.2020
Product Items
| Catalog Nr. | Product Name |
| 128.08 | TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit, 8 preps |
| 128.24 | TraPR Small RNA Isolation Kit, 24 preps |
| 135.08 | Small RNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina with TraPR, 8 preps |
| 135.24 | Small RNA-Seq Library Prep Kit for Illumina with TraPR, 24 preps |